GENOTYPING POLYPLOIDS USING MOLECULAR TAGS
Would you like to explore the possibilities for obtaining a license for this technology? You can contact our licensing team by mail. Would you like to know more about our technologies and licensing possibilities? Visit our webpage about Licensing KeyGene’s proprietary technologies.
Invention
The invention provides a method for genotyping polyploids and probes for use in this method. These probes are characterized in that they comprise unique molecular indices (UMIs). Using a mixture of uniquely tagged oligo ligation probes, effective genotyping of 326 SNPs was proven in tetraploid genomic samples in a KeyGene® SNPSelect assay.
Benefit
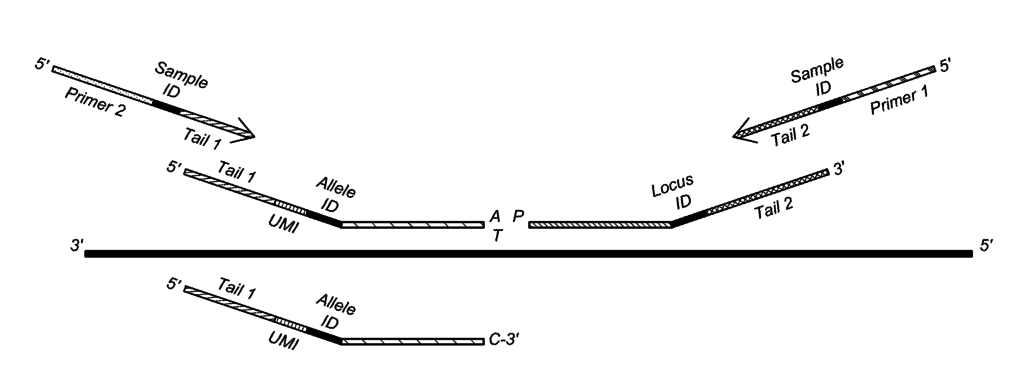 Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Accurate determination of the genotyping of polyploids requires the quantification assessment of the presence of specific alleles. As many genotyping assays require amplification, genotyping polyploids is cumbersome as alleles may amplify unevenly. The probes of the invention, in particular the oligo ligation probes, provides for a flexible solution and allow for effective genotyping up to genotyping thousands of SNPs simultaneously with high concordancy rates. Probe design and genotyping are automated. Together with KeyGene’s invention on probe amplification, the invention allows for a very cost-effective genotyping method.
Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Accurate determination of the genotyping of polyploids requires the quantification assessment of the presence of specific alleles. As many genotyping assays require amplification, genotyping polyploids is cumbersome as alleles may amplify unevenly. The probes of the invention, in particular the oligo ligation probes, provides for a flexible solution and allow for effective genotyping up to genotyping thousands of SNPs simultaneously with high concordancy rates. Probe design and genotyping are automated. Together with KeyGene’s invention on probe amplification, the invention allows for a very cost-effective genotyping method.
Vision
The invention results in a more accurate calling of the genotypes as a single error in base calling will not result in wrong allele-calling. When using the UMI approach, genotyping of polyploid samples is more accurate, while maintaining flexibility in the number of samples and the number of SNPs. SNPSelect has the capabilities to use one single technology for SNP-calling in a low multiplex context up to a very high multiplex setting.
Patent
Click on the link below for an overview of the patent family in the European Patent Register:
Please note that the European Patent Register may not be extensive and/or accurate, for which KeyGene is not responsible. Please contact your patent expert for further information.